Let CSS know when you scroll. No JavaScript needed.
Scroll-state queries let you style elements based on how a container is scrolled. You can detect when it’s at the top, bottom, or in motion, and trigger animations directly from CSS.
Here’s a simple example:
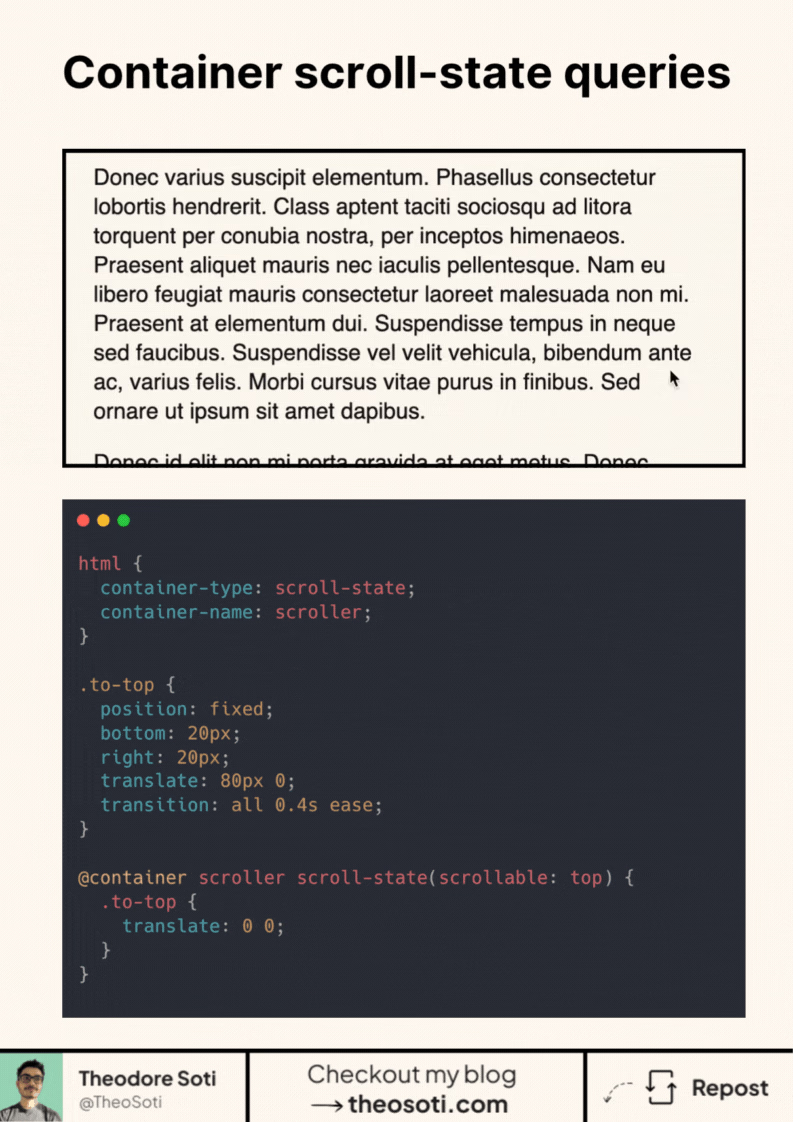
html {
container-type: scroll-state;
container-name: scroller;
}
.to-top {
position: fixed;
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
translate: 80px 0;
transition: all 0.4s ease;
}
@container scroller scroll-state(scrollable: top) {
.to-top {
translate: 0 0;
}
}The key is container-type: scroll-state.
It makes the page a scroll container that CSS can observe.
The @container rule reacts to its scroll state.
When the container is at the top, bottom, or being scrolled, styles update automatically.
No scroll listeners. No intersection observers. Just CSS responding to motion.
You can use it to fade headers, slide elements, or trigger transitions as users scroll.
Browser support is about 68.5%, so it’s still experimental, use with caution (or don’t use it yet).
This is a glimpse of a more reactive CSS. Less scripting, more design freedom.
Scroll state queries are practical for sticky headers, section indicators, and context-aware controls. Because the state is declarative in CSS, you can remove a lot of JS scroll bookkeeping and keep behavior easier to maintain.
Scroll state queries are practical for sticky headers and section-aware controls. Since state logic stays in CSS, you can reduce JS scroll bookkeeping and keep behavior easier to audit.
Always include reduced-motion behavior. A strong animation pattern is one that degrades cleanly while preserving meaning.
For teams, container-type: scroll-state is easiest to maintain when it starts in one documented example before broader reuse. This keeps implementation predictable and prevents style drift as the codebase grows.
If you liked this tip, you might enjoy the book, which is packed with similar insights to help you build better websites without relying on JavaScript.
Go check it out https://theosoti.com/you-dont-need-js/ and enjoy 20% OFF for a limited time!